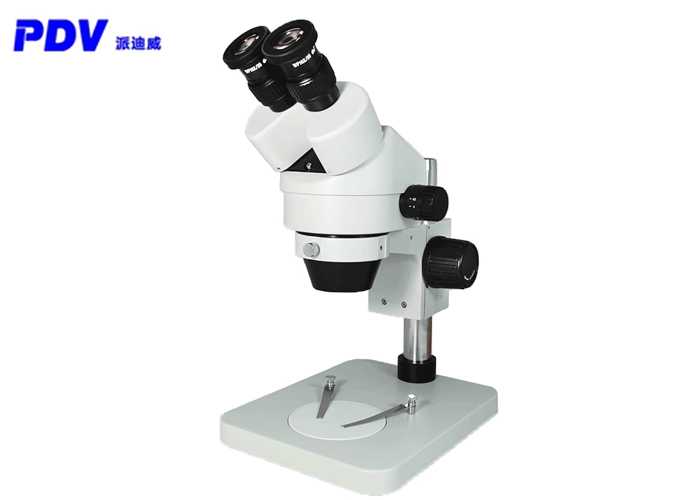
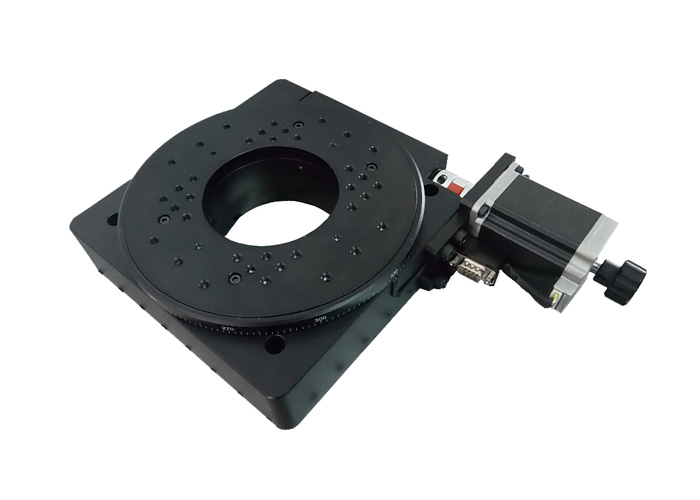
This article describes a kind of rotating table, adopting a high-precision electric rotating table, new structure, new technology; the key indicators have been strictly tested to reach the international level of similar products.
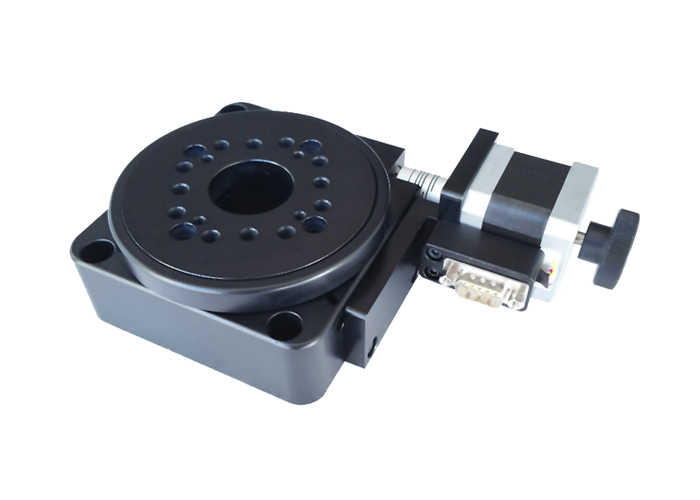
This series of products are used in laser precision processing, three-dimensional scanning measurement systems, etc. The worm wheel uses durable friction materials and imported super steel shafts to achieve high-precision, high-load stable motion. The outer ring has a scale and interfaces for easy signal output. Standard stepper motor and DB9 interface, choose a flexible controller. A conventional stage with a stepper motor and RS232 interface can be easily connected to a motion controller. Provides a compact, cost-effective motion control solution that can be used for laser processing applications of various powers.
When faced with laser applications that require high-precision control of laser power, users generally have two choices.
First, they can use lasers with variable output power, such as Q-switched lasers, fiber lasers, or femtosecond lasers. With these lasers, the optical power can be easily changed on the laser source without the need for a separate laser power attenuation device.
Second, users do not choose a variable power laser source, or their application requires an additional laser power control method. Under these conditions, users need a simple, cost-saving solution that can generate continuously variable laser power from the input laser source. In this scenario, an auxiliary optical system that can attenuate the laser power is required.
Many laser applications require optical power adjustments in the process. For example, measuring high-power lasers with only photodiodes requires significant beam attenuation to avoid saturation or damage to the sensor. When different materials require different beam powers to achieve and maintain the required interaction with the laser beam, power attenuation is also necessary. In some applications, a narrow and variable laser power range may be required to minimize the adverse effects of the heat-affected zone or its size.
Another example of the need to control the laser power is to scan a laser beam on a substrate with a variable thickness or a curved shape, and the effective scanning speed needs to be changed to adjust the effective laser power deposition. In many cases, a variable power laser can be used. However, variable power lasers exhibit unacceptable pulse stability and beam quality changes at low operating currents and power levels. Therefore, for applications that require pulse stability and maintain the original laser beam parameters at lower power, coupling a fixed power laser source with an auxiliary laser power attenuation optical system is often the most economical solution.
The easiest way to attenuate the power of the laser beam is to use an absorption filter that can attenuate the beam to a certain degree. Absorption filters can achieve a constant degree of attenuation, such a device can achieve a constant degree of attenuation in a relatively wide wavelength range. You can use a strip or disc filter with a step or continuous optical density change along its long side (linear filter) or around its rotation axis (filter wheel) to achieve a step or continuous change Light attenuation.
However, when the absorption filter is used to attenuate the laser beam, the absorbed power will be converted into heat, which will cause thermal effects, for example, the thermal lens effect will distort the spatial profile of the laser beam. For high-power lasers, thermal effects can even destroy the filter. These problems have caused absorption filters to not be used in many laser applications. At the same time, the laser power can also be attenuated in another way, reflecting at Brewster's angle to produce a beam with a few percent of the original laser power. Although this method can be used in some applications, it reduces the linear polarization of the laser beam.

In addition, it is difficult to produce continuously varying attenuation in this way. There are also some optical fiber methods for laser power attenuation. These methods are dedicated to optical fiber communication systems and are not widely used in other places. The most widely used, simple, and economical method of linearly polarized laser beam power attenuation is to use a ½ wave plate and a polarizer to provide a continuously variable laser power attenuation function for the laser beam, where the wavelength range and power of the laser beam Determined by the application.
Tips
1. Turntable transmission ratio. 180:1 or 90:1 or 45:1.
2. The stepper motor driver card is purchased separately.
3. If you need to add zero on the electric turntable, please tell us that the standard product is not zero.
4. The stage has a distal and proximal limit switch.
If you need a zero switch, please contact us in advance.














