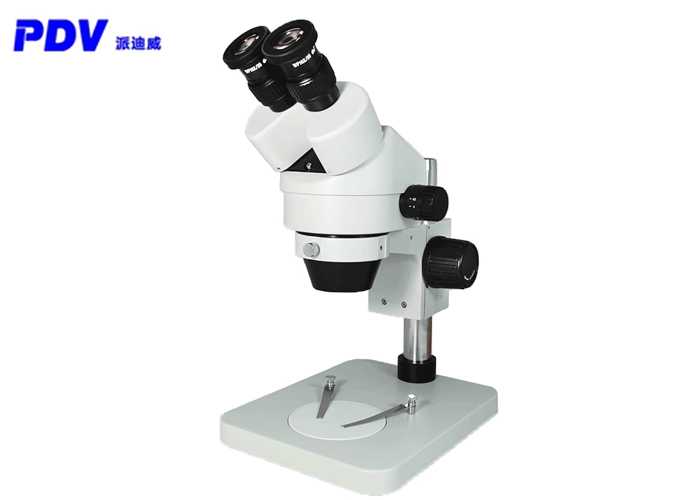
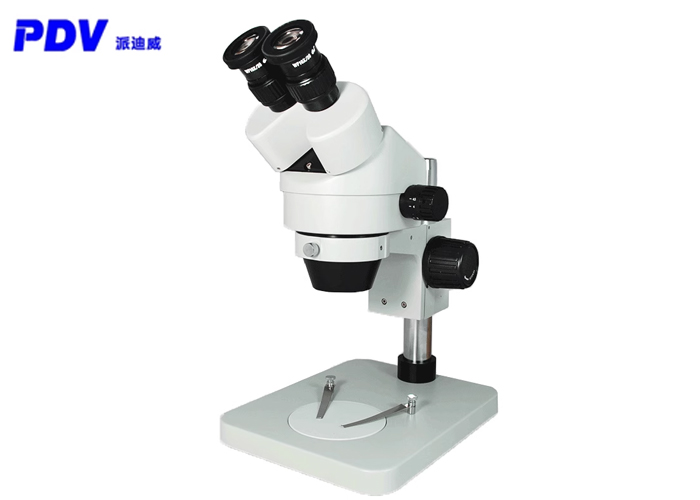
A stereo microscope, also known as a "solid microscope" or "dissecting mirror", can produce upright three-dimensional images when observing objects. It has strong stereo perception, clear and wide imaging, and long working distance. It is a conventional microscope with a very wide range of applications. Convenient operation, intuitive operation, and high verification efficiency. It is suitable for the inspection of electronic industry production lines, the verification of printed circuit boards, the verification of soldering defects (printing misalignment, collapse, etc.) in printed circuit components, the verification of single-board PCs, and vacuum fluorescence Verification of display screen VFD, etc., equipped with measurement software can measure various data.
(1) After installing the microscope, plug in the power plug, turn on the power switch, and select the lighting method after ensuring that the power supply voltage is consistent with the microscope's rated voltage;
(2) According to the specimen to be observed, select the platen (for transparent specimens, use frosted glass platen; for opaque specimens, use black-and-white platen), put it into the base plate hole, and lock it;
(3) Loosen the fastening screw on the focusing slide seat and adjust the height of the lens body. The visual working distance is about 80mm, (make it the working distance roughly the same as the selected objective lens magnification), and then lock it. Bracket, close the safety ring to the focusing bracket and lock it;
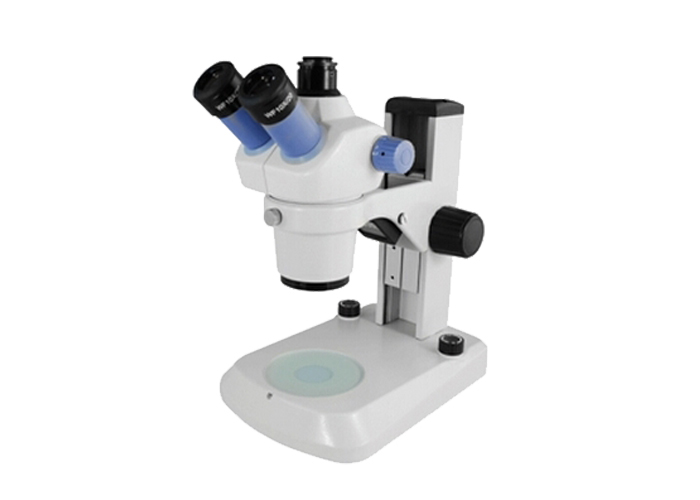
(4) After installing the eyepiece, loosen the screw on the eyepiece tube first, and then tighten the screw after installing the eyepiece (when putting the eyepiece into the eyepiece tube, be careful not to touch the surface of the lens);
(5) Adjust the interpupillary distance. When the user observes the field of view through two eyepieces that are not a circular field of view, he should pull the two prism boxes to change the exit pupil distance of the eyepiece tube so that one can be observed. Fully coincident circular field of view (indicating that the interpupillary distance has been adjusted);
(6) Observe the specimen (adjust the focus of the specimen). First, adjust the diopter circle on the left eyepiece tube to the 0-marked position. Under normal circumstances, first observe from the right eyepiece tube (that is, the fixed eyepiece tube), turn the zoom tube (for models with a zoom device) to the highest magnification position, and turn the focusing handwheel to focus the specimen until the specimen’s After the image is clear, turn the zoom barrel to the lowest magnification position. At this time, use the left eyepiece tube to observe. If it is not clear, adjust the diopter circle on the eyepiece tube axially until the specimen image is clear, and then binocular Observe the focusing effect;
(7) When the observation is over, turn off the power, remove the specimen, and cover the microscope tightly with a dust cover.
The above information is provided by a stereo microscope supplier.













